by Mitchell Rose, Billtrust Senior Vice President & General Manager, Corporate Segment
This article originally appeared in the Q4 2021 issue of CRF Perspective.
What is the average collection period formula?
The average collection period, also known as the "average accounts receivable aging period," is a financial term used to measure the length of time it takes a company to collect payments from its customers. In other words, the average collection period is the amount of time a person or company has to repay a debt. For example, the average collection period for debt in America is about 30 days. There are various ways to calculate average collection periods, such as when a payment is due and made, but the most practical is through the average collection period formula. This data can determine how well a company is managing its cash flow.

How to calculate the average collection period: formula
The average collection period is the average amount of time a company will wait to collect on a debt. The average collection period formula involves dividing the number of days it takes for an account to be paid in full by 365 days, the total number of days in a year.
Number of days = 365 ÷ Amount owed
Because the amount of time a company has to collect on debt changes yearly, the average collection period is a crucial calculation to help you determine how long debt collection typically takes.
For example:
In some years, the company will have more time to collect on that debt, and in other years it might be less. This way, companies can use this formula to determine how many days they have until they need to start charging interest on unpaid debts.
Average collection period and accounts receivable turnover
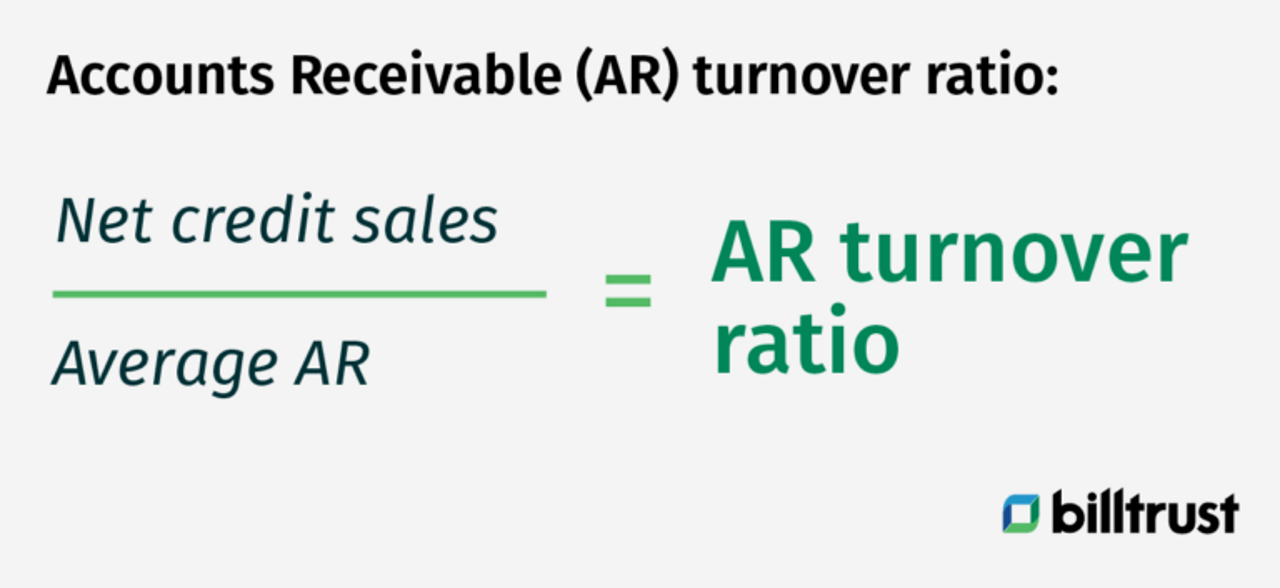
Accounts receivable turnover indicates the amount of time between the sale and the final receipt of cash. In accounting, when a company is calculating the average collection period, the number is needed to gain insight into how long a company will have before collecting its receivables. The accounts receivable (AR) turnover directly correlates to how long it will take to collect on funds owed by customers.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio is calculated by dividing total net credit sales by average accounts receivable.
Need to calculate net credit sales?
Net credit sales equal sales on credit minus sales returns minus sales allowances.

The average collection period formula gives an average of past collections, but you can also use it as a gauge for future calculations of how long collections take. Lower ratios mean faster average collection periods, indicating efficient management. The higher the ratio, the longer it takes to manage a budget.
Why calculate the average collection period formula?
You know that the average collection period formula can calculate the average number of days it takes to collect debts, but just how is an average collection period calculation crucial to your company’s financial well-being? The average collection period formula will also help you:
- Understand when a company’s receivables will be collected
- Determine which credit terms are best for your company
- Provides a benchmark for when to write off a debt as uncollectable
- Gain insight into how long your customers are taking to pay their debts and if they are paying them quickly enough for you to grow your business
- Gauge your company's creditworthiness
- Give you a starting point at which to begin tracking and shortening your collection periods for increased yearly profits
How to shorten your average collection period
Looking to shorten the average time to receive payments for a smoother payment flow? Below are a few simple steps to help you reduce your average collection periods:
1) Analyze your cash flow.
Cash flow is the lifeblood of any business, but it can be hard to manage when you're in the midst of a cash flow crisis. A common problem for small businesses is paying suppliers. The most common reasons for this are late payments to vendors or slow collections from customers. Begin by getting a sense of where you are with an overall cash flow analysis.
2) Look for ways to optimize your cash flow.
If you are having trouble paying your bills, it's essential to look for ways to improve cash flow. This includes analyzing your collection periods for optimization so that you get paid after providing goods or services.
3) Offer discounts.
To incentivize faster payments, you can offer discounts if the client pays within a specific time frame. Providers could also provide incentives for early payments or apply late fees to those who do not make their payments on time. This will shorten your average collection period.
4) Streamline customer invoicing.
Another way to optimize the average collection period is to streamline your customer invoicing. This can be done with the help of an automated AR service, like Billtrust, to ensure that your billing stays fast, which frees you to focus on the more significant elements of your business.
Key takeaways from the average collection period formula

A crucial metric for any business is the average collection period, a measure of how long it takes a customer to pay their bill. The average collection period formula, in turn, is critical for measuring a company's collectability. The longer collections take, the less profitable each transaction will be, potentially leading to some serious financial troubles.
Why track collections with a formula?
The average collection period formula assesses how well they're managing their debt portfolio and whether they need to improve their collections strategy. It also provides an idea of how long an overdue account will take to recover if it's not collected in time, which ultimately helps the company decide when it should write off an account as uncollectible, determine favorable credit terms, gauge corporate creditworthiness and determine a starting point for collections optimization.
Looking to shorten your average collection period?
Consider using an automated AR service, such as Billtrust, to help you analyze and optimize your cash flow, while also streamlining customer invoicing.

