Efficient ERP payment processing has become a cornerstone of business success. As organizations navigate increasing transaction volumes, diverse payment methods, and complex compliance requirements, the need for streamlined, automated payment processing services has never been more pressing. Finance leaders face mounting pressure to modernize their payment systems while maintaining security, compliance, and operational efficiency. The following sections will explore the fundamental components of ERP payment processing, examine key challenges, and provide actionable strategies for optimizing your payment operations through automation and best practices.
Understanding ERP payment processing
ERP payment processing is the integration of payment transactions within Enterprise Resource Planning systems. This encompasses more than simple payment execution - it's an approach to managing the entire financial transaction lifecycle. From initial invoice creation through final reconciliation, modern ERP payment processing serves as the backbone of financial operations, connecting various business processes into a cohesive workflow.
- Digital transformation: The accelerating pace of digital transformation has fundamentally changed how businesses handle payments. Organizations that cling to manual processes find themselves at a significant competitive disadvantage, struggling with inefficiencies that more digitally mature competitors have long since eliminated. The ability to process payments efficiently through ERP systems has become a key differentiator in market performance.
- Global commerce: Modern business operations frequently span multiple countries, currencies, and regulatory environments. ERP payment processing must adapt to handle these complexities while maintaining efficiency and compliance. This includes managing various payment formats, understanding regional banking requirements, and navigating different tax implications across jurisdictions.
- Cash flow optimization: Maintaining optimal cash flow requires sophisticated payment processing capabilities. Modern ERP systems provide the visibility and control needed to manage working capital effectively, ensuring businesses can make strategic decisions about when and how to process payments.
The current state of B2B payments
The B2B payment landscape has evolved significantly, moving far beyond traditional check-based systems to encompass a range of digital B2B payment methods and processing requirements.
- Payment diversity: The modern B2B payment ecosystem includes everything from traditional ACH transfers to sophisticated virtual card solutions. Each payment method brings its own processing requirements, integration challenges, and reconciliation needs. Organizations must maintain the flexibility to handle current payment methods while being prepared for emerging technologies.
- Integration challenges: Many businesses operate with multiple systems that need to communicate easily. This includes ERP systems, banking platforms, accounts payable solutions, and various payment processors. The complexity of these integrations often creates bottlenecks in payment processing workflows.
- Manual processes: Despite technological advances, many organizations still rely heavily on manual intervention for payment processing. This includes manual data entry, payment approval workflows, and reconciliation processes. These manual touchpoints create inefficiencies and increase the risk of errors.
Read the blog → What you need to know about Virtual Credit Cards
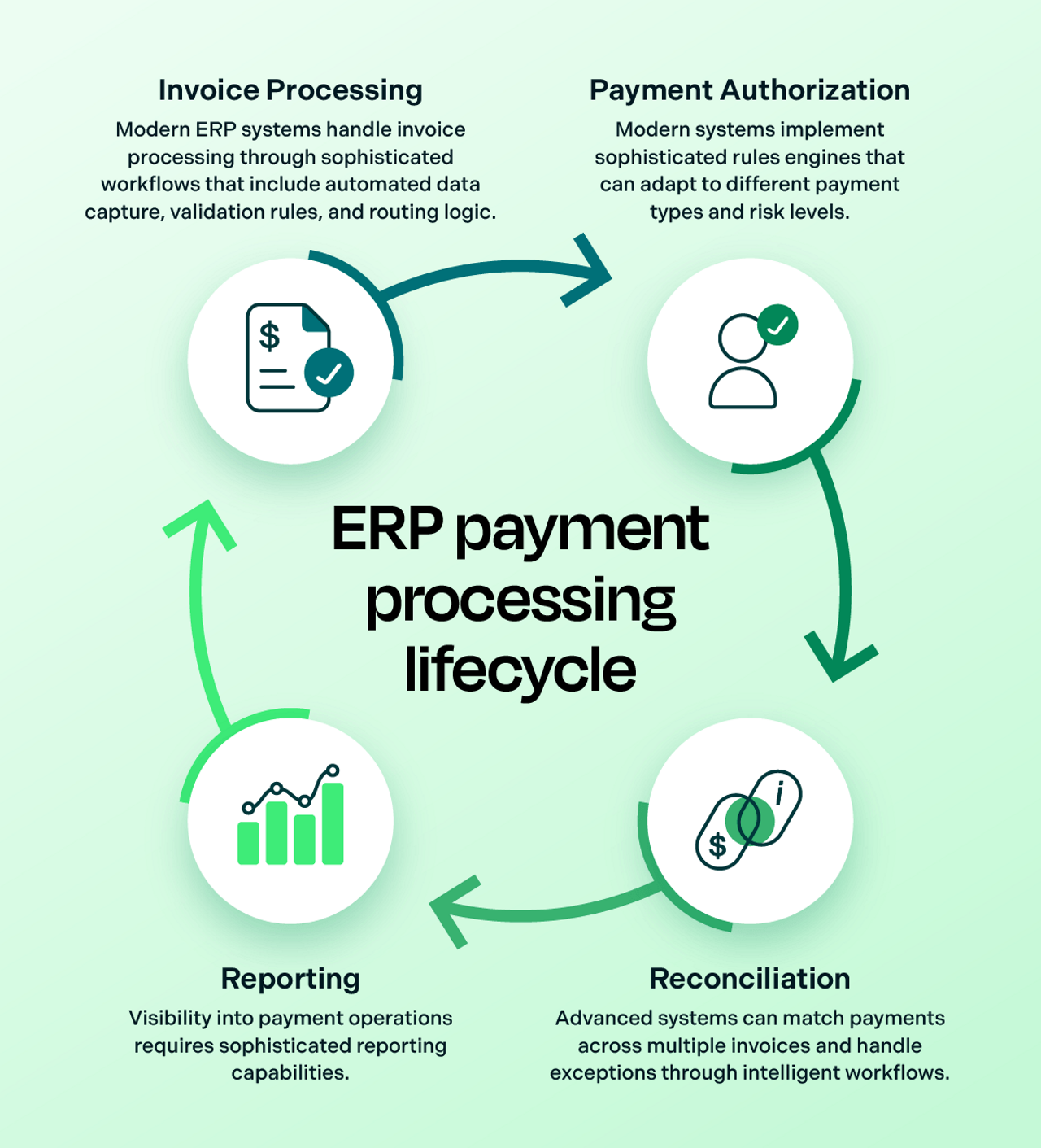
ERP payment processing fundamentals
Understanding the core components of ERP payment processing requires a deep dive into several key areas:
- Invoice processing: Modern ERP systems handle invoice processing through sophisticated workflows that include automated data capture, validation rules, and routing logic. This extends beyond simple document creation to include complex matching algorithms and exception handling processes.
- Payment authorization: Security and control in payment processing require authorization workflows. This includes multi-level approval processes, segregation of duties, and automated fraud detection measures. Modern systems implement sophisticated rules engines that can adapt to different payment types and risk levels.
- Reconciliation: Automated reconciliation capabilities have evolved to handle complex scenarios including partial payments, payment batching, and cross-currency financial transactions. Advanced systems can match payments across multiple invoices and handle exceptions through intelligent workflows.
- Reporting: Visibility into payment operations requires sophisticated reporting capabilities. This includes real-time dashboards, customizable reports, and analytical tools that provide insights into payment trends and operational efficiency.
Common challenges in ERP payment processing
Organizations frequently encounter several significant obstacles in their payment processing operations:
- Data quality issues: Payment processing relies heavily on accurate data across multiple systems. Poor data quality, inconsistent formats, and incomplete information create significant challenges in automated processing. This includes issues with vendor master data, payment instructions, and remittance information.
- System limitations: Many organizations struggle with legacy ERP systems that lack modern payment processing capabilities. These limitations often force companies to implement manual workarounds or maintain multiple systems to handle different payment requirements.
- Resource constraints: Implementing and maintaining sophisticated payment processing systems requires specialized expertise. Many organizations struggle to maintain the necessary technical and operational resources to optimize their payment processes.
Benefits of automated ERP payment processing
The transition to automated payment processing delivers transformative benefits across multiple dimensions of financial operations.
- Process efficiency: Automated systems eliminate manual data entry and reconciliation tasks, transforming multi-day processing cycles into near-instantaneous operations. Finance teams can process higher payment volumes without adding staff, while existing team members can focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine tasks.
- Error reduction: Automation reduces common payment processing errors such as duplicate payments, incorrect amounts, and misrouted financial transactions. By implementing validation rules and automated matching algorithms, organizations can catch and prevent errors before they impact operations.
- Cash flow management: Real-time payment processing and automated reconciliation provide immediate visibility into cash positions. Finance leaders can make more informed decisions about payment timing, take advantage of early payment discounts, and better manage working capital.
- Resource optimization: By automating routine payment tasks, finance teams can redirect their efforts toward value-added activities such as financial analysis, vendor relationship management, and strategic planning. This shift from transactional to strategic work enhances the finance function's contribution to business success.
- Customer experience enhancement: Automated payment processing enables organizations to offer their customers more payment options, faster processing times, and better visibility into payment status. This flexibility and transparency strengthen business relationships and improve customer satisfaction.
- Business intelligence: Automated systems capture detailed payment data that can be analyzed to identify trends, optimize payment terms, and improve forecasting accuracy. This intelligence helps organizations make better decisions about payment strategies and vendor relationships.
Key features of modern ERP payment solutions
Today's integrated payment solutions incorporate sophisticated capabilities that go far beyond basic payment processing.
- Intelligent payment routing: Advanced systems automatically determine the optimal payment method based on factors such as cost, speed, and vendor preferences. This routing maximizes efficiency while minimizing processing costs.
- Automated reconciliation: Modern solutions employ AI-powered matching algorithms that can handle complex scenarios such as partial payments, payment batching, and cross-currency transactions. These systems can achieve high match rates even with imperfect remittance data.
- Multi-entity support: Sophisticated payment solutions can manage complex organizational structures, handling payment processing across multiple legal entities, currencies, and banking relationships while maintaining appropriate controls and visibility.
- Smart workflows: Configurable approval workflows adapt to different payment types, amounts, and risk levels. These workflows can incorporate multiple approval levels, delegate authorities, and automatic escalations.
- Vendor management: Vendor portals allow suppliers to maintain their own payment information, submit invoices, and track payment status. This self-service capability reduces administrative burden while improving vendor satisfaction.
- Payment optimization: Advanced analytics help organizations optimize payment timing, method selection, and working capital management. These tools can identify opportunities for early payment discounts while improving cash flow requirements.
Best practices for ERP payment processing
Implementing these proven best practices ensures optimal results from payment automation initiatives.
- Standardization: Establish consistent payment processes across all business units and payment types. This standardization simplifies training, reduces errors, and improves control effectiveness.
- Exception management: Develop clear procedures for handling payment exceptions, including automated routing of issues to appropriate personnel and tracking of resolution times.
- Performance monitoring: Implement monitoring of payment processing metrics, including processing times, error rates, and automation levels. Regular review of these metrics helps identify improvement opportunities.
- API-First approach: Prioritize solutions that offer API capabilities for integration with other systems. This approach provides flexibility for future changes while maintaining real-time data synchronization.
- Data governance: Establish strong data governance practices to ensure payment data quality and consistency across systems. This includes standardized formats for vendor information, payment instructions, and remittance data.
- Security integration: Ensure payment security measures integrate with existing security infrastructure while maintaining processing efficiency.
Implementation considerations
Successful implementation requires careful attention to several key factors.
- Current state assessment: Document existing payment processes, including pain points, manual workarounds, and control weaknesses. This assessment provides the foundation for improvement planning.
- Stakeholder engagement: Involve all affected departments early in the planning process. This includes not just finance and IT, but also procurement, legal, and business units that will be impacted by payment process changes.
- Technology evaluation: Consider both current and future requirements when selecting payment solutions. This includes scalability needs, integration capabilities, and support for emerging payment methods.
- Phased implementation: Break the implementation into manageable phases, starting with high-impact, lower-risk areas. This approach allows organizations to demonstrate quick wins while managing change effectively.
- Training strategy: Develop training programs that address both system operation and process changes. Include ongoing support mechanisms to help users adapt to new ways of working.
- Risk management: Implement appropriate controls and testing procedures to ensure payment security and accuracy during the transition to new processes.
Steps to optimize your ERP payment processing
Follow these key steps to achieve payment processing excellence:
- Process analysis: Begin with a review of your current payment operations. This involves mapping every step of your existing payment workflows, from invoice receipt through reconciliation. Document pain points, manual touchpoints, and control gaps in your current processes. Work with key stakeholders to understand operational challenges and gather improvement suggestions from those closest to the day-to-day operations.
- Technology evaluation: Conduct an assessment of your current technology landscape and future needs. This includes reviewing your ERP system's payment processing capabilities, identifying integration points with other systems, and understanding any technical limitations. Consider both immediate requirements and future scalability needs when evaluating potential solutions.
- Gap analysis: Compare your current capabilities against industry best practices and your organization's strategic objectives. This analysis should cover process efficiency, control effectiveness, compliance requirements, and user experience. Identify areas where automation can deliver the greatest impact in terms of cost reduction and efficiency improvement.
- Solution design: Develop a solution that addresses identified gaps and aligns with your strategic objectives. This includes defining required system functionality, integration requirements, and control frameworks. Consider both technical and operational aspects when designing your target state solution.
- Business case development: Create a detailed business case that outlines expected benefits, required investments, and implementation timeline. Include both quantitative benefits like cost savings and qualitative improvements such as enhanced control effectiveness. Consider both direct and indirect benefits when building your business case.
- Implementation roadmap: Create a detailed plan for implementing your selected solutions. Break the implementation into manageable phases that minimize business disruption while delivering steady progress. Consider dependencies between different components and align the implementation sequence accordingly.
- Change management planning: Develop an approach to managing the organizational impact of new payment processes. This includes communication strategies, training programs, and support mechanisms to ensure successful adoption. Consider the needs of different user groups when planning change management activities.
- Execution strategy: Implement changes following your planned roadmap while maintaining flexibility to adjust based on feedback and results. This includes coordinating technical implementations, process changes, and user training. Maintain clear communication channels throughout the execution phase.
- Performance monitoring: Establish clear metrics to track the success of your optimization efforts. This includes both operational metrics like processing times and strategic measures like cost reduction. Use these metrics to identify areas needing adjustment and demonstrate program value.
- Continuous improvement: Maintain an ongoing focus on identifying and implementing process improvements. Regular reviews of performance metrics, user feedback, and emerging technologies can help identify new optimization opportunities. Create mechanisms for capturing and acting on improvement suggestions from users.
Compliance and security considerations
Modern payment processing requires security and compliance measures.
- Payment security: Implement end-to-end payment encryption, secure authentication mechanisms, and audit trails. These measures protect sensitive payment data while maintaining processing efficiency.
- Compliance framework: Develop a compliance framework that addresses payment regulations across all operating jurisdictions. This includes payment card industry standards, data protection requirements, and regional payment regulations.
- Control environment: Establish strong internal controls over payment processing, including segregation of duties, approval workflows, and regular control testing.
- Multi-layer security: Implement multiple security layers including encryption, authentication, and fraud detection. This defense-in-depth approach provides protection for payment operations.
- Access management: Establish role-based access controls that limit system access based on job requirements while maintaining processing efficiency.
- Continuous monitoring: Implement real-time monitoring of payment activities to detect and prevent unauthorized or suspicious transactions.
The future of ERP payment processing lies in intelligent automation, integration, and adaptive technologies that can evolve with changing business needs. Organizations that invest in modernizing their payment processing capabilities position themselves for improved efficiency, better cash flow management, and enhanced competitive advantage.
Empowering financial excellence: about Billtrust
For over two decades, Billtrust has been at the forefront of transforming how businesses manage their order-to-cash processes. As the leading provider of automated accounts receivable solutions, we help organizations gain efficiencies, accelerate cash flow, and drive profitability through innovative technology and deep industry expertise.
Our mission is simple but powerful: we help businesses get paid faster. Through our unified, end-to-end accounts receivable platform, we process over $1 trillion in invoice dollars annually for more than 2,400 customers worldwide. Our comprehensive solution suite tackles the entire order-to-cash cycle, from credit management and invoicing to payments and cash application.
We're more than just a technology provider – we're a partner in your financial success. Our team of experts works alongside yours to ensure you achieve optimal results from our solutions, whether you're looking to control costs, accelerate cash flow, or improve customer satisfaction.
Ready to learn how Billtrust can help your business? Contact our team today to discover the power of automated accounts receivable.
Frequently Asked Questions
Check out the FAQs for general questions. Find helpful answers quickly to get the information you need.
Key considerations include encryption, access controls, fraud detection, audit trails, and compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Success requires comprehensive training, clear communication of benefits, ongoing support, and a phased implementation approach that allows users to adapt gradually.
Key metrics include processing cost reduction, staff time savings, error rate reduction, and improvements in days payable outstanding (DPO). Speaking with an expert helps identify which metrics are most important for your business and how they can be impacted by automation.


