Electronic payment processing has become a cornerstone of modern business operations. As B2B payment volumes continue to grow year over year, organizations are increasingly seeking ways to optimize their payment processes while maintaining security and efficiency. This guide explores how finance leaders can leverage electronic payment solutions to drive business growth and operational excellence.
The current state of B2B electronic payments
The B2B payments landscape is undergoing a dramatic transformation. Traditional paper-based processes are giving way to digital solutions, with organizations prioritizing electronic payment adoption.
Digital transformation in payment processing has accelerated significantly, driven by:
- Increased demand for real-time payment capabilities
- Growing need for enhanced security measures
- Rising expectations for integration with existing systems
- Expanding global trade requirements
- Pressure to reduce operational costs
How electronic payments impact business operations
Electronic payments fundamentally reshape how businesses operate, affecting everything from cash flow management to customer relationships. Companies transitioning from paper-based to electronic payment methods consistently report significant cost savings and processing time improvements.
Key impact areas include:
- Connection with leading invoice software platforms
- Streamlined accounts receivable processes
- Reduced manual intervention and human error
- Improved cash flow visibility
- Enhanced security and fraud prevention
- Better customer experience and satisfaction
- Increased operational efficiency
Understanding electronic payment types
Modern finance leaders need to understand various electronic payment methods to optimize their payment stack. Here's a comprehensive breakdown of key payment types:
- ACH payments: Automated Clearing House transfers form the backbone of B2B electronic payments, offering a cost-effective solution for recurring transactions. These bank-to-bank transfers provide a reliable, secure method for processing regular payments while maintaining detailed transaction records.
- Wire transfers: While more expensive than ACH, wire transfers provide same-day settlement and are ideal for high-value, time-sensitive transactions. They offer immediate availability of funds and are particularly useful for international transactions, making them essential for global business operations.
- Virtual card payments: Single-use virtual credit cards provide enhanced security and control over B2B payments. They generate unique card numbers for each transaction, reducing fraud risk while offering valuable rebates and rewards. This modern payment method is gaining traction among businesses seeking to optimize their working capital.
- Real-time payments (RTP): The newest addition to the payment ecosystem, RTP networks enable instant, 24/7 payment processing. They're particularly valuable for time-critical payments and improved cash flow management, offering unprecedented speed and transparency in transaction processing.
- eCheck processing: Electronic versions of paper checks combine familiar formats with digital efficiency. They provide a bridge between traditional and modern payment methods, making them particularly appealing to businesses transitioning to digital processes.
- Digital wallet solutions: Emerging as a versatile option for B2B payments, digital wallets offer convenient, secure payment processing with enhanced reporting capabilities. They're increasingly being adopted for their ability to streamline payment operations and reduce processing costs.
Read the blog → E-invoicing and compliance updates June 2024
Electronic payment infrastructure
A robust electronic payment infrastructure forms the foundation of successful digital payment operations. Key components include:
- Payment gateways and processors: These essential components serve as the backbone of electronic payment systems, handling the secure routing and processing of transactions across multiple channels. Modern gateways provide real-time authorization capabilities, sophisticated fraud detection tools, and processing across various payment methods, ensuring smooth transaction flow while maintaining security and reliability.
- Integration capabilities: The ability to connect and synchronize with existing business systems is crucial for operational efficiency. This includes ERP system connectivity, real-time AI accounting software synchronization, and API-driven architecture that enables automated reconciliation and data flow across the entire payment ecosystem, reducing manual intervention and improving accuracy.
- Security framework: A comprehensive security framework protects sensitive financial data and transactions through multiple protective layers. This includes end-to-end encryption, advanced tokenization methods, multi-factor authentication systems, and continuous compliance monitoring to ensure adherence to industry standards and regulations while protecting against emerging threats.
- Network connectivity: Strong network infrastructure enables efficient communication between various financial systems and institutions. This includes connection to business payment networks, banking system integration, support for cross-border payment processing, and real-time settlement capabilities, ensuring fast and reliable transaction processing across global markets.
Strategic benefits of electronic payments
The adoption of electronic payments delivers multiple strategic advantages that directly impact an organization's bottom line and operational efficiency.
- Cost reduction analysis: Electronic payments significantly reduce processing costs by eliminating manual handling, paper-based processes, and associated labor costs. Companies typically see substantial savings in check processing, mailing expenses, and staff time allocation.
- Cash flow acceleration: Digital payment methods speed up the entire payment cycle, from invoice to settlement. Faster processing times and automated systems help businesses access their funds more quickly, improving cash position.
- Working capital optimization: Electronic payment solutions provide better visibility and control over payment timing, enabling organizations to optimize their working capital strategy. This improved control allows businesses to better manage their cash positions and take advantage of early payment discounts.
- Reconciliation efficiency: Automated matching and reconciliation capabilities dramatically reduce the time and effort required to process payments. This automation helps eliminate manual errors and provides real-time visibility into payment status.
- Customer satisfaction improvements: Modern payment solutions offer customers greater flexibility in payment methods and timing. Self-service portals and automated invoicing and payment options enhance the customer experience while reducing support requirements.
- Environmental impact: By reducing paper usage and physical transportation needs, electronic payments help organizations meet their sustainability goals while simultaneously cutting costs.
Implementation considerations
Successful electronic payment implementation requires careful planning and consideration of several key factors:
- Integration requirements: A thorough assessment of your current technology ecosystem is essential for successful implementation. This begins with evaluating ERP compatibility and API connectivity needs, followed by data migration planning. Organizations must develop testing protocols to ensure seamless integration with existing systems while maintaining data integrity and operational continuity throughout the transition process.
- Staff training needs: Training programs are vital for ensuring successful adoption and utilization of new payment systems. This involves identifying specific user roles and developing targeted training curricula that address each role's unique requirements. Organizations must establish ongoing support resources and implement performance monitoring systems to ensure staff maintain proficiency and adapt to system updates over time.
- Change management strategies: Effective change management minimizes disruption during implementation. This includes developing clear stakeholder communication plans and detailed process documentation. Organizations should create realistic transition timelines, implement risk mitigation strategies, and establish clear success metrics to track progress and demonstrate value to stakeholders.
- Customer adoption approaches: Successfully transitioning customers to electronic payment systems requires a strategic combination of education and support. This includes developing comprehensive awareness programs and creating appropriate incentive structures to encourage adoption. Organizations must establish support systems, implement feedback collection mechanisms, and maintain adoption tracking methods to ensure successful customer transition.
- Security considerations: Robust security measures must be implemented to protect sensitive financial data and transactions. This encompasses implementing strong data encryption protocols, establishing strict access controls, and developing comprehensive fraud prevention measures. Organizations need to maintain detailed audit trails and establish clear incident response plans to address potential security breaches.
- Compliance requirements: Meeting regulatory and industry standards is essential for electronic payment implementation. Organizations must ensure adherence to relevant regulatory frameworks and industry standards while maintaining proper documentation procedures. Regular compliance audits should be scheduled, and systems must be in place to monitor and implement required updates to maintain ongoing compliance.
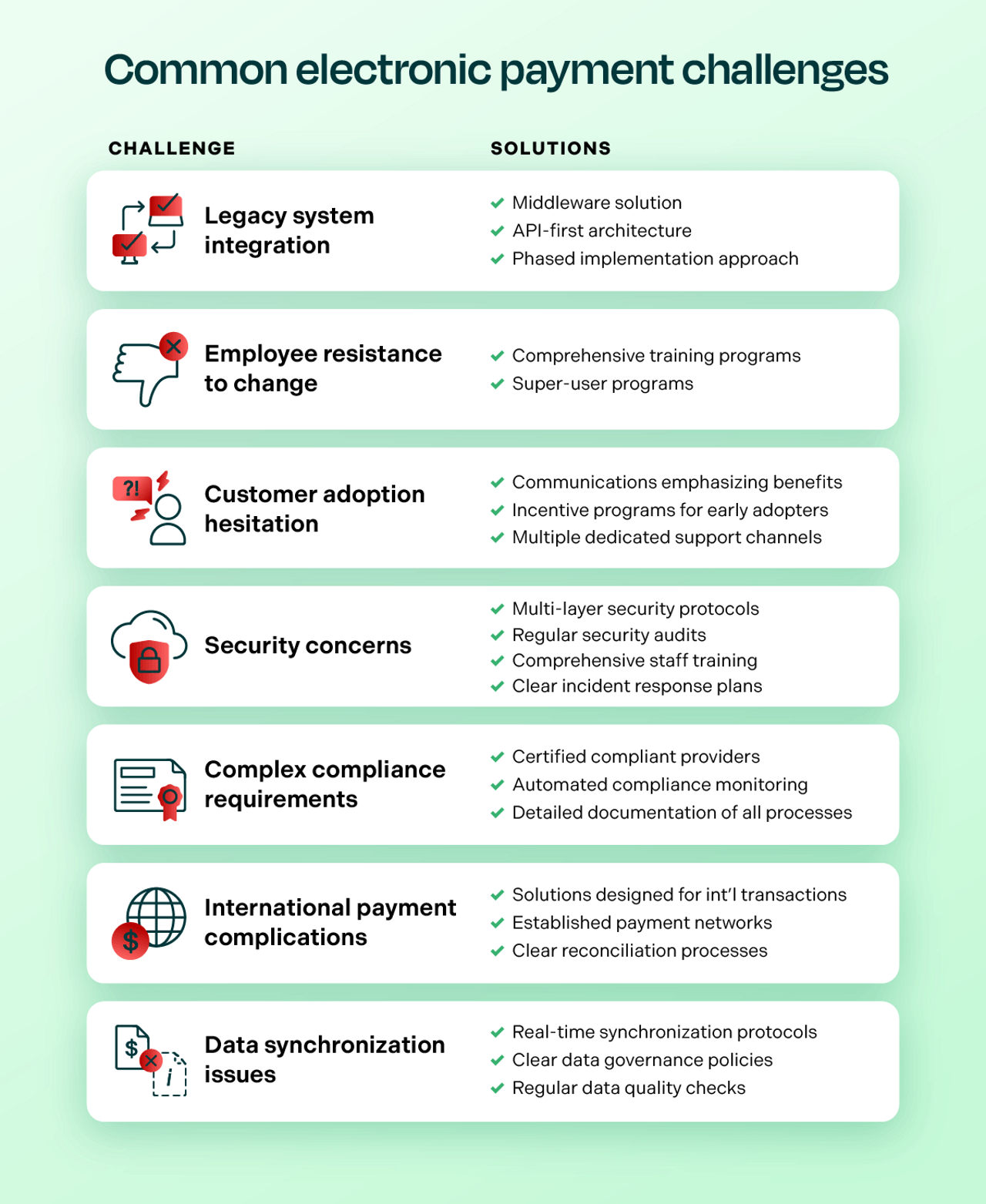
Common challenges and solutions
The transition to electronic payment systems, while beneficial, often presents organizations with hurdles to overcome. Understanding these common challenges and their proven solutions can help finance leaders develop more effective implementation strategies and minimize potential disruptions to their operations. Here are the key challenges organizations typically face and practical approaches to addressing them:
- Legacy system integration: One of the most challenging hurdles organizations face is integrating modern payment solutions with existing legacy systems. Many businesses operate on decades-old infrastructure that wasn't designed for today's digital payment landscape. To address this challenge, organizations can implement middleware solutions that act as bridges between old and new systems, adopt API-first architectures that allow for gradual modernization, and utilize phased implementation approaches that minimize disruption to existing operations.
- Employee resistance to change: Staff members often resist new payment systems due to comfort with existing processes and fear of job security. Organizations can overcome this by implementing comprehensive training programs that emphasize how automation handles routine tasks while elevating employees' roles to more strategic work. Creating super-user programs where tech-savvy staff members champion the new system and provide peer support has proven particularly effective in building confidence and adoption.
- Customer adoption hesitation: Many customers are reluctant to change their payment methods due to perceived complexity or security concerns. Success in overcoming this challenge comes from developing clear communication strategies that emphasize benefits like faster payment processing and improved account visibility. Implementing incentive programs for early adopters, providing dedicated support during transition periods, and offering multiple channels for assistance helps ensure smooth customer migration to new payment systems.
- Security concerns: The digital nature of electronic payments raises legitimate security concerns about fraud and data protection. Organizations can address these fears by implementing multi-layer security protocols including end-to-end encryption, tokenization, and multi-factor authentication. Regular security audits, comprehensive staff training on security best practices, and maintaining clear incident response plans help build confidence in the system's security measures.
- Complex compliance requirements: Meeting various regulatory standards across different jurisdictions can be overwhelming. The solution lies in partnering with payment providers who maintain current compliance certifications and automatically update their systems to meet evolving requirements. Implementing automated compliance monitoring tools and maintaining detailed documentation of all processes helps ensure ongoing adherence to regulatory standards.
- International payment complications: Cross-border payments introduce challenges with currency conversion, different banking systems, and varying regulatory requirements. Organizations can navigate these complexities by implementing payment solutions specifically designed for international transactions, utilizing established payment networks that handle currency conversion and compliance requirements, and developing clear processes for managing international payment reconciliation.
- Data synchronization issues: Maintaining consistent data across multiple systems and payment channels can be challenging. Organizations can address this through implementing real-time synchronization protocols, establishing clear data governance policies, and utilizing automated reconciliation tools. Regular data quality checks and automated error detection systems help maintain data integrity across the payment ecosystem.
Best practices for implementation
Successful implementation of electronic payment systems requires a structured approach focusing on key operational areas. Here are the essential best practices that organizations should consider:
- Strategic planning: A well-defined implementation strategy serves as the foundation for success. This involves establishing clear, measurable objectives aligned with business goals, creating realistic timelines that account for all implementation phases, and allocating appropriate resources including budget, personnel, and technology. Organizations should also establish specific success metrics to track progress and demonstrate ROI, ensuring these metrics align with both immediate operational needs and long-term strategic objectives.
- Stakeholder engagement: Active involvement of all relevant parties throughout the implementation process is crucial for success. This means identifying and engaging key stakeholders early in the planning phase, maintaining regular communication through structured updates, and establishing clear channels for feedback collection. Organizations should create a transparent reporting system that shares progress, challenges, and wins, helping maintain momentum and support throughout the implementation journey.
- Technology selection: Choosing the right electronic payment solution requires careful evaluation and planning. Organizations should begin with a comprehensive needs assessment that considers current requirements and future growth plans, followed by thorough vendor evaluation that examines not just features but also support capabilities and financial stability. The selection process should include detailed integration planning and careful consideration of scalability to ensure the chosen solution can grow with the organization.
- Risk management: A proactive approach to risk management helps prevent potential issues and ensures smooth implementation. This involves conducting thorough risk assessments across all aspects of the implementation, developing comprehensive mitigation strategies for identified risks, and establishing clear contingency plans for potential disruptions. Regular review and updates of risk management protocols ensure continued effectiveness as the implementation progresses and new challenges emerge.
- Project governance: Establishing clear oversight and accountability mechanisms ensures the implementation stays on track and achieves desired outcomes. This includes creating a dedicated project management structure, defining clear roles and responsibilities, and establishing regular review cycles to monitor progress and address issues promptly. Effective governance also includes developing change control procedures and maintaining comprehensive documentation throughout the implementation process.
- Change readiness: Preparing the organization for the transition to new payment systems is essential for success. This involves assessing organizational readiness across all affected departments, developing targeted change management strategies, and ensuring adequate support resources are available. Organizations should focus on building internal champions, providing comprehensive training, and maintaining clear communication channels throughout the transition period.
This guide provides finance leaders with the essential knowledge needed to successfully implement and optimize electronic payment solutions. As the business landscape continues to evolve, staying current with electronic payment technologies and best practices becomes increasingly crucial for maintaining competitive advantage and operational efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
Check out the FAQs for general questions. Find helpful answers quickly to get the information you need.
Successful customer adoption of electronic payments requires a strategy that combines clear communication, meaningful incentives, and support throughout the transition process. Organizations should start by developing a clear communication plan that explains the benefits and features of electronic payments, supported by practical demonstrations and real-world examples of successful implementations. Offering meaningful incentives such as early adoption discounts, faster payment processing, or reduced fees for electronic transactions can help overcome initial resistance to change. A strong support structure is essential, including a dedicated support team during the transition period and multiple channels for assistance. Regular check-ins with key customers and quick resolution of any issues help maintain momentum and build confidence in the new system. The most successful adoption strategies also include regular collection and implementation of customer feedback, allowing for continuous improvement of the system based on actual user experiences.
When evaluating electronic payment solutions, organizations should prioritize integration capabilities that guarantee connection with existing business systems and processes. The ideal solution should offer API functionality with thorough documentation, supporting both real-time data synchronization and batch processing capabilities. Integration with major ERP systems, accounting software, and CRM platforms is essential, as is the ability to connect with inventory management systems and legacy infrastructure. The solution should provide flexible data import/export options and automated reconciliation tools, all built on a scalable architecture that can grow with your business. Look for platforms that offer custom field mapping capabilities and the ability to handle complex data relationships while maintaining data integrity across all integrated systems.


