This post was originally published in June 2020 and was updated in October 2024, with additional information about autonomous cash application processes, including the benefits of AI-driven invoice matching, machine learning for continuous improvement, and more.

What is cash application?
Cash application is the process of matching a payment from a customer to the corresponding invoice being paid in the seller's accounts receivable ledger. It is an essential part of accounts receivable management.
Cash application is a critical component of the accounts receivable process, focusing on matching incoming payments to the appropriate customer invoices. It involves identifying, reconciling, and accounting for payments received from clients against their respective outstanding invoices. This process ensures accurate financial records, enables businesses to maintain healthy cash flow, and plays a pivotal role in managing the overall accounts receivable ledger. By effectively applying cash, companies can accurately forecast their financial health, minimize errors in accounting, and improve relationships with their customers by acknowledging payments in a timely manner.
How Is cash application used?
Cash application is used by businesses as a fundamental step in their financial transaction management to ensure that payments received are accurately recorded and allocated. This can involve manually processing checks and electronic payments or utilizing automated cash application software to streamline the process. By accurately applying cash, businesses can significantly reduce the amount of unapplied cash on their books, decrease days sales outstanding (DSO), and enhance their working capital management. Automated systems can leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to match payments to invoices, even when remittance information is incomplete or missing, thereby reducing manual intervention and increasing efficiency.
The use of cash application extends across industries, serving as a backbone for healthy financial operations and allowing companies to maintain clear insights into receivables performance.
Read now → Track your receivables performance with days sales outstanding [ Blog ]

What are the elements of cash application?
The main elements of cash application are as follows:
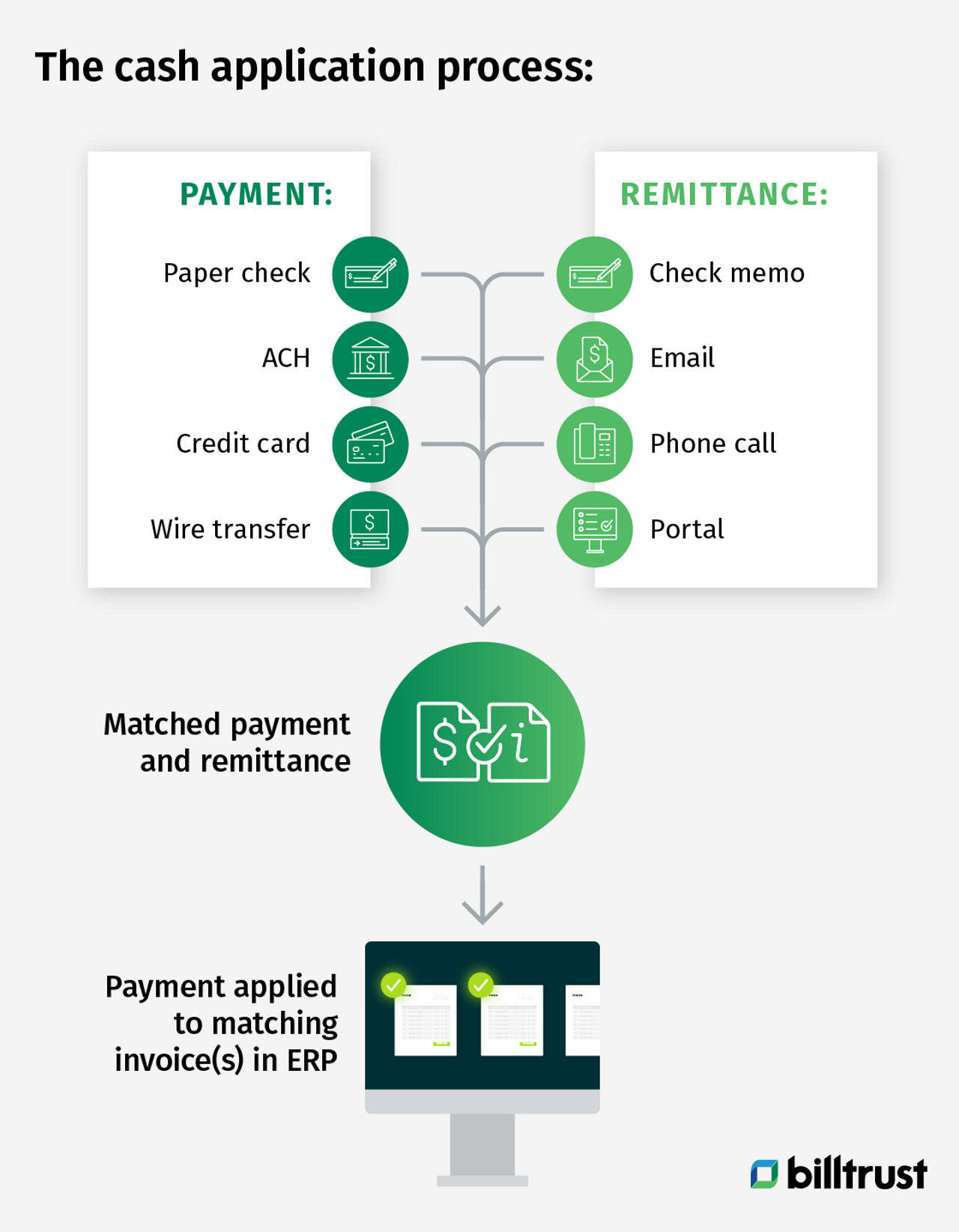
Payment: The payment is the funds transferred from the buyer to the supplier. Payments come in many forms. Paper payments include paper checks. Electronic payments include wire transfers, ACH, procurement card and virtual credit card payments.
Remittance advice: Also known simply as remittance, remittance advice is the data that describes why a payment is being made. Remittance advice can include the invoice number or numbers that the funds are paying off. It can also include other information about the payment, for example, it could include a note that the buyer is only paying 75% of the invoiced amount because the delivered products were damaged.
Remittance advice is sometimes included alongside payment, i.e. a paper check with the invoice number written in the memo section, but remittance can also be transferred separately from the payment in an email, phone call or web portal.
Invoice: The invoice is the original bill that prompted the payments to be made. A cash application specialist uses the remittance advice to understand what invoices are being paid by the funds transferred from the buyer.
Once the cash application specialist has “matched” the payment to the invoice(s), they will mark the invoice(s) as paid in the supplier's Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system.
What makes cash application complex?
In the past, when the vast majority of B2B payments were made by paper check, cash application was a relatively simple, though laborious process. Paper checks have remittance advice printed typically have the remittance advice printed right below the check itself, so cash application specialists were able to match those checks to their corresponding invoices.
But electronic payments have many advantages over check and have become more popular. Electronic payments often do not come with remittance advice attached – it is often sent separately in an email, phone call, fax or buyer’s portal.
Now, cash application specialists have to first connect the payment to the remittance advice and only THEN can they match the payment and remittance to the invoice.
Compounding this are the complications of payments meant to pay off multiple invoices, short pays due to discounts or disputes and errors in remittance advice.
Why is cash application important?
When a company receives a payment, they must apply it in order to be sure that they have a right to those funds. Once a company knows the funds are rightfully theirs, they can then use that money to fund payroll, make investments or disburse profits to shareholders. The faster they can apply cash, the faster they can use it.
Most B2B sales are made on credit. This means that the supplier agrees to deliver a product or service to the buyer with payment expected at a later date. This is called extending credit. But a responsible supplier will not extend an infinite amount of credit to a buyer. They will set a limit based on many factors. When a buyer uses their entire line of credit to make a purchase from a supplier, they cannot make another purchase until the invoice associated with their purchase is paid off. If a buyer sends a payment to a supplier, but the supplier’s cash application process is slow, then replenishment of the buyer’s credit will be delayed, and the supplier will miss out on sales they could have made between the moment they received the buyer’s payment and their application of the funds and replenishment of buyer credit.
Read now → Avoid short-pay situations with streamlined cash application processes [ Blog ]
Different types of cash application
Cash application is an essential aspect of the accounts receivable process, where payments received are matched and posted against relevant invoices. This process ensures that a business's accounts receivable ledger is accurate, reflecting the real-time status of customer payments. Given the variety of payment methods and customer types, companies may employ different cash application processes. Understanding these can help businesses streamline operations, reduce manual work, and improve cash flow. Here are some of the principal types of cash application processes:
- Manual cash application
Overview: Manual cash application is the traditional method, where finance teams physically match incoming payments to open invoices. This often involves sifting through bank statements, checks, and remittance advice, followed by manual entry into the accounting system.
Challenges: It is time-consuming, prone to human error, and becomes inefficient with scale. - Semi-automated cash application
Overview: A semi-automated process incorporates some level of automation, such as using electronic remittance advices (ERAs) or employing basic software that helps in identifying matches between payments and invoices. It reduces the manual effort required but still needs human intervention for exceptions and verification.
Benefits: It improves efficiency and accuracy over purely manual processes but is still limited in handling complex scenarios or large volumes efficiently. - Fully automated cash application
Overview: Fully automated cash application uses advanced software solutions, incorporating technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), to completely automate the matching process. It processes payments regardless of format, automatically matches them to invoices, and updates the accounts receivable ledger in real-time.
Benefits: Significantly reduces manual labor, decreases the error rate, improves cash flow visibility, and can handle large volumes of transactions efficiently. - Bank lockbox services
Overview: In a bank lockbox service, customers send their payments to a PO box that is accessed by the business’s bank. The bank processes these payments directly and provides the business with detailed information for updating their accounts receivable.
Benefits: Reduces processing time and speeds up the cash application cycle. However, it involves additional bank fees and still requires manual posting of details into the business’s financial system. - Electronic payment portals
Overview: Many businesses now offer electronic payment options through customer portals, where customers can pay invoices directly. These systems are designed to automatically apply the received funds to the correct invoice, often allowing customers to allocate payments themselves.
Benefits: Increases efficiency, accelerates the payment process, and enhances customer experience by offering convenience and flexibility in payment options. - Mobile payment applications
Overview: The use of mobile payment solutions is on the rise, where payments are made through mobile devices using specialized apps. These systems can integrate with accounting software to apply cash automatically.
Benefits: They offer convenience and speed in processing payments, and when integrated with accounting software, they can streamline the cash application process further.
The choice of cash application process depends on various factors, including the volume of transactions, the complexity of payment methods, available technology infrastructure, and the strategic goals of the business. Moving from manual to more automated cash application processes can significantly impact a company’s operational efficiency, accuracy, and ability to manage its cash flow effectively. As technology advances, the trend is clearly towards more automation, leveraging AI and ML to handle repetitive tasks, allowing finance teams to focus on more strategic activities.
How can I improve cash application?
Automation is essential to improving a company's cash application process. Many companies are already using some degree of automation in their cash application.
It is very common for companies to use bank lockboxes to receive check payments. Banks read their incoming checks either with data entry specialists or with robots and digitize the payment and remittance information. The banks will then transfer this payment and remittance data to the company’s ERP. The ERP system will generally have some ability to match the payments and remittance data to open invoices in the system.
But ERPs are not optimized for this process and they will generally not be able to match payments meant for multiple invoices, payments sent without remittance or short pays to open invoices.
The rate at which an automated solution can match payments to invoices with no human intervention is referred to as a “match rate.”
Electronic payments often come without remittance advice attached. When remittance is sent separately, most ERPs cannot match incoming electronic payments to open invoices without human intervention.
But in recent years, A/R automation vendors have made great strides in creating specialized cash application automation software. Cash application automation software integrates with a business’ ERP system to match incoming payments regardless of channel to their appropriate open invoices. When payments can be accepted and matched with no human intervention, it is referred to as straight-thru-processing (STP).
Modern cash application automation vendors can achieve match rates near 100%. Even the process of resolving disputes over partial payments can be improved by the machine learning enabled cash application software.
To learn how accounts receivable automation can improve your cash application process, connect with Billtrust.
Unveiling the future: the autonomous cash application revolution
In the dynamic realm of accounts receivable and financial management, the emergence of autonomous cash application processes marks a significant leap toward operational efficiency and precision. This groundbreaking approach leverages cutting-edge technology to transform how businesses handle their cash application, making the entire process more streamlined, accurate, and virtually hands-free. Here's an in-depth exploration of what an autonomous cash application process entails and the benefits it brings to the table.
An autonomous cash application process is built upon the foundation of advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Robotic Process Automation (RPA). These technologies work in concert to automatically match customer payments to relevant invoices without human intervention, thus revolutionizing traditional cash application methodologies.
- AI-Driven invoice matching
The process starts with the use of AI algorithms that scan incoming payments and related remittance information. By accessing and analyzing data from various sources — bank statements, emails, EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) messages, and payment portals — the system identifies the payer and the exact invoices being settled. This capability far exceeds manual or semi-automated methods in both speed and accuracy. - Machine learning for continuous improvement
Machine learning algorithms are at the heart of autonomous cash application systems. They learn from every transaction, continually refining their ability to match payments to invoices with minimal or no discrepancies. Over time, these systems become more adept at handling exceptions, recognizing patterns, and predicting potential issues before they arise, thus minimizing the need for manual oversight.
To learn how accounts receivable automation can improve your cash application process, connect with Billtrust.
Read now → Improve cash flow with cash flow forecasting insights [ Blog ]
FAQ
A cash account application refers to the process of applying received cash payments to the correct customer accounts and invoices within a company's financial system.
The risks of the cash application process include potential errors in payment matching, delayed application of payments leading to inaccurate financial records, and the risk of fraud if the process is not securely managed.

